Diagnosing 'learning bugs'
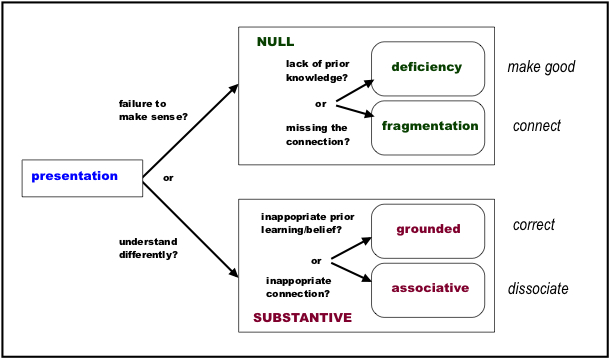
The typology of learning impediments is a model of the different types of 'learning bugs' that may occur when our teaching does link to students' thinking in the ways we intend. The model was developed in the context of science teaching (developing 'Science Learning Doctors') but has much wider applications.
The main distinction is between
Null learning impediments - where The intended learning may not take place because the student is unable to make sense of the teaching in terms of existing ideas
and
Substantive learning impediments - where Learning may occur which does not match the intended learning because the student interprets teaching in terms of existing ideas in a different way to intended
Null learning impediments, where the intended learning does not take place because the student is unable to make sense of the teaching in terms of existing ideas, come in two main types:
Deficiency learning impediments - which may be because the student has never acquired the necessary pre-requisite knowledge,
and
Fragmentation learning impediments when the student may simply not recognise how their existing ideas are relevant
Substantive Learning Impediments occur where learning does not match the intended learning because the student interprets teaching in terms of existing ideas in a different way to intended. These may also be of two main types:
Grounded learning impediments - which occur because existing understanding is inconsistent with accepted scientific thinking,
and
Associative learning impediments - which may occur because the student makes an unintended (and unhelpful) link with prior learning
Grounded learning impediments occur because existing understanding is inconsistent with accepted scientific thinking. Such ‘alternative conceptions’ may derive from various sources:
Associative learning impediments occur because the student makes an unintended link with prior learning. These may be of various types:
The typology may be used as a guide to questioning students to identity the nature of specific learning bugs, and so to respond accordingly:

Image reproduced from Taber, 2006: The Science Learning Doctor’s Guide. (download the Learning Doctor 'Guidebook')
Return to ECLIPSE homepage
List of science topics

Dr Keith S Taber kst24@cam.ac.uk
University of Cambridge Faculty of Education
© Keith S Taber, 2012